Oceanologia No. 39 (4) / 97
Contents
Papers
Papers
Numerical studies of the influence of the benthic detritus pool on the chlorophyll a concentration in a stratified sea
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 339-376
Lidia Dzierzbicka-Głowacka, Andrzej Zieliński
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Keywords: Biological model, Phytoplankton, Nutrient, Benthic regeneration
Manuscript received December 9, 1997, in final form December 29, 1998.
Abstract
This paper presents the numerical simulations of variability
of biological processes such as phytoplankton bottom flux, remineralisation
of detritus, detrital material sedimenting out of the water column onto the
bottom and the benthic detritus pool, as well as the effect of these
processes
on the distribution functions of chlorophyll a and nutrient
concentration in a stratified sea. The influence of these processes on the
distribution functions was recorded in the changes in biological and chemical
parameters, such as the factor limiting production increase, the maximum rate
of production increase, the nutrient half-saturation constant and the
function
characterising the vertical distribution of zooplankton. The numerical
studies were carried out using a phytoplankton-phosphate-detritus
biological
model with a well-developed regeneration mechanism. This paper presents
the
vertical distributions of biological characteristics to facilitate a better
understanding of temporal changes but on the assumption that the above
processes are horizontally uniform. The calculations were made in an area
0 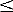 z
z 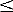 20 m with a vertical space step of 10 cm and a time step of
15 min. The complex experimental data, gathered during the PEX ´ 86
international scientific experiment of the Baltic states, and subsequently
by the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea, were used as
the input data for the calculations.
20 m with a vertical space step of 10 cm and a time step of
15 min. The complex experimental data, gathered during the PEX ´ 86
international scientific experiment of the Baltic states, and subsequently
by the International Council for the Exploration of the Sea, were used as
the input data for the calculations.
`IO PAS initial model´ of marine primary production for remote
sensing applications
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 377-395
Bogdan Wożniak, Jerzy Dera
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Roman Majchrowski, Dariusz Ficek
Pedagogical University, Słupsk
Olga J. Koblentz-Mishke
Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow
Mirosław Darecki
Institute
of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Keywords: Primary production, Bio-optical modelling, Photosynthesis, Quantum yield,
Nutrients, Remote sensing, World Ocean
Manuscript received October 23, 1997, in final form November 10, 1997.
Abstract
A model of marine primary production with a set of statistical
relationships linking physiological parameters of the
phytoplankton with abiotic factors of the sea has been
developed. The study is based on empirical data analysed from
some 3500 stations in various oceanic regions. The data comes
from Polish and Russian expeditions as well as from literature.
A thin oil film covering the sea surface as a modifier of the downward transmission of light
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 397-411
Zbigniew Otremba
Department of Physics, Maritime Academy, Gdynia
Keywords: Sea surface, Crude oil pollution, Light reflection, Light transmission,
Model remote sensing
Manuscript received December 5, 1997, in final form January 12, 1998.
Abstract
Selected results of investigations into the optical
properties of thin oil films on a sea surface are
presented. The plots of angular functions are given for
the coefficient of the reflection of the light arriving
at the sea surface from the depths and for the
coefficient of transmission of the light entering the
water across an oil film. The calculations on a
triple-layer model (air-oil-water) takes into account the
results of temperature measurements and the spectral
relationships of the complex refractive index for two
optically diverse types of crude oil - Petrobaltic and
Romashkino.
Chlorophyll a and its derivatives in recent sediments of the southern Baltic Sea collected in the years 1992-1996
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 413-432
Grażyna Kowalewska
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Keywords: Chlorophyll a, Chlorophyll a derivatives, Chlorins,
Phytoplankton pigments, Sediments, Baltic Sea, HPLC
Manuscript received October 28, 1997, in final form December 15, 1997.
Abstract
Determinations of chlorophyll a and its derivatives (chlorins)
as well as chlorophylls b, c and β-carotene in recent sediments
(0-10 cm) of the southern Baltic Sea carried out in the years 1992-1996
are compiled. Correlations of the concentrations of chlorins with parameters such
as the origin of a sample, oxygen in near-bottom waters (literature data)
and organic carbon in sediments were analysed with respect to the chlorins
utility as environmental markers. Comparison of the concentration levels of
chlorins in sediments with the literature results proves that these compounds
are sensitive environmental markers of primary production in the overlying
waters (taking local water currents into account) and of environmental
conditions. Moreover, together with other sedimental pigments, they are
markers of prevailing plankton classes in the adjacent waters, and are
valuable indicators of the average plankton composition supplementary to
biological determinations.
Small-scale vertical distribution of zoobenthos in the sandy littoral of the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 433-446
Ashraful Mohammed Haque
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Maria Szymelfenig
Institute of Oceanography, Gdańsk University, Gdynia
Jan Marcin Węsławski
Institute of Oceanology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Sopot
Keywords: Sandy littoral, Zoobenthos
Manuscript received September 30, 1997, in final form December 11, 1997.
Abstract
Three sites in the Gulf of Gdańsk were analysed for the
presence of zoobenthos in 0-10 cm sediment cores, collected
at 1 m depth in the course of the year. 80% of the macrobenthos
biomass was distributed in the top 5 cm of the sediment at
Oslonino, while at Jurata 50% of the biomass was found below 5 cm.
At Mikoszewo macrofauna was found in the intermediate 3-5 cm layer only.
Meiofauna was most abundant in the upper sediment layers at Jurata
and Oslonino, while at Mikoszewo most of the biomass was found below 5 cm.
The upper 5 cm layer was the richest in taxa, as regards both meio- and
macrobenthos. Below 5 cm Polychaeta dominated the macrofauna,
Nematoda and Oligochaeta the meiofauna. The vertical distribution of
meio- and macrofauna changes slightly in the course of the year.
The spring and autumn samples revealed more fauna in the upper
sediment layers, while the deeper sediment strata were rich in
biomass in the winter months. The mean size of individual zoobenthos
specimens increased with the depth of the sediment layer.
Macrozoobenthos of the sandy littoral zone of the Gulf of Gdańsk
Oceanologia 1997, no. 39 (4), pp. 447-460
Lech Kotwicki
Institute of Ecology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Dziekanow Lesny
Keywords: Gulf of Gdańsk, Sandy littoral zone, Macrozoobenthos,
Seasonal changes
Manuscript received October 10, 1997, in final form November 14, 1997.
Abstract
The aim of the study was to determine the distribution,
composition and seasonal variability of the macrozoobenthos
in the sandy littoral zone of the Gulf of Gdańsk including the inner
part of Puck Bay. The results of qualitative and quantitative
investigations of the benthic fauna are presented. Material was
collected every month from October 1992 to December 1993 at 10 stations
from 0.5 to 1 m depth. A total of 23 species and 5 higher macrofaunal
taxa were identified. At each station 2 samples were collected with an
80 cm2 Morduchaj-Boltovski pipe-grab. The average abundance
and wet weight of particular taxa were calculated. The analyses
showed that in the shallow-bottom zone the most diverse and
abundant bottom fauna occurred at the stations situated in the
inner Puck Bay. The composition was least diverse at the stations
located in the estuary of the river Vistula (Swibno, Mikoszewo.
Polychaeta and Bivalvia constituted up to 97% of the bottom fauna biomass;
Nereis diversicolor and Mya arenaria were the dominant species.